high-temperature creep-fatigue behavior of alloy 617|617 creep fatigue : traders Abstract: This paper presents the high-temperature creep-fatigue testing of a Ni-based superalloy of Alloy 617 base metal and weldments at 900 C. Creep-fatigue tests were . web17 de dez. de 2016 · Radio Garden Lets You Tune Into 8,000 Stations From Around The World : Goats and Soda : NPR. Goats and Soda. STORIES OF LIFE IN A CHANGING WORLD. Offbeat. Radio Garden Lets You Tune Into.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB1 de out. de 2018 · 概述:. TEMPI综合症是与浆细胞肿瘤相关的副肿瘤综合症之一(另一是POEMS综合症),其特征是毛细血管扩张(telangiectasia),促红细胞生成素增高和红细胞增多症(elevated erythropoietin and erythrocytosis),单克隆丙种球蛋白病(monoclonal gammopathy),肾脏周围积液 .
This paper presents the high-temperature creep-fatigue testing of a Ni-based superalloy of Alloy 617 base metal and weldments at 900 °C. Creep-fatigue tests were conducted with fully reversed axial strain control at a total strain range of 0.6%, 1.2%, and 1.5%, and peak tensile .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant .Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant .Abstract: This paper presents the high-temperature creep-fatigue testing of a Ni-based superalloy of Alloy 617 base metal and weldments at 900 C. Creep-fatigue tests were . This paper presents the high-temperature creep-fatigue testing of a Ni-based superalloy of Alloy 617 base metal and weldments at 900°C. .
Authors have construct a 3D creep-fatigue-elasticity damage interaction diagram based on life prediction model for the analysis of creep-fatigue interaction behavior of various .The fatigue and creep-fatigue behavior of Alloy 617 is initially investigated in air at 950°C at 0.3% and 0.6% total strain ranges. Future work will include testing in a VHTR controlled helium .
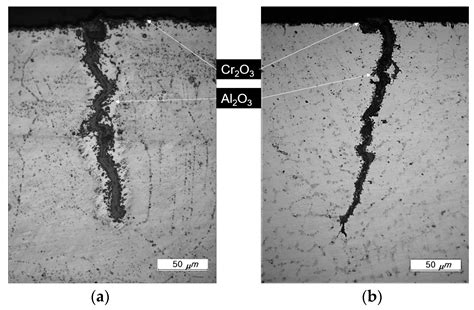
high temperature aluminum creep fatigue
A new in-situ biaxial creep-fatigue testing system was built to study the creep-fatigue interaction of Alloy 617, a nickel base alloy with potential structural applications in the .Experimental results revealed that the axial strain ratcheting and cyclic hardening/softening responses of Alloy 617 vary significantly with temperature levels, strain rates and strain . Alloy 617 is the leading candidate material for an intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) of the very high temperature reactor (VHTR), expected to have an outlet temperature as high .
To better understand and address these issues, Low Cycle Fatigue (LCF) and creep-fatigue tests of alloy 617 and alloy 230 were conducted in this study. Creep-Fatigue life .Alloy 617 is the leading candidate material for an Intermediate Heat Exchanger (IHX) of the Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR). To evaluate the behavior of this material in the expected .High Temperature Nuclear Reactor (VHTR), expected to have an outlet temperature as high as 950°C. Acceptance of Alloy 617 in Section III of the ASME Code for nuclear construction requires a detailed understanding of the creep-fatigue behavior. Initial creep-fatigue work on Alloy 617 suggests a more Abstract. Alloy 617 is the leading candidate material for an intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) of the very high temperature reactor (VHTR), expected to have an outlet temperature as high as 950°C. Acceptance of Alloy 617 in Section III of the ASME Code for nuclear construction requires a detailed understanding of the creep-fatigue behavior. Strain .
Creep behavior of the Inconel 617 alloy has been investigated through tests carried out in the temperature range of 650 °C to 800 °C under 95 to 350 MPa. Creep curves obtained from tests on the alloy exhibit a non-classical nature, with the primary creep rate decreasing to a minimum value, followed by a typical increase, which is either continuous at .
Therefore, the creep-fatigue behavior of Alloy 617 requires systematic investigation for its qualification as the structural material for IHX applications in VHTR. . High-temperature creep-fatigue of Alloy 617 base metal and weldments. In: ASME 2007 pressure vessels and piping conference 2007 Jul 22. American Society of Mechanical Engineers .High Temperature Multiaxial Creep-Fatigue and Creep-Ratcheting Behavior of Alloy 617 Shahriar Quayyum, Mainak Sengupta, Gloria Choi, Clifford J. Lissenden, and Tasnim Hassan Abstract Nickel based Alloy 617 is one of the leading candidate materials for intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) of the next generation nuclear plant (NGNP). The operating temperature of IHX will be in the creep regime of Alloy 617 and low-cycle creep-fatigue and creep-ratcheting failure mechanisms of Alloy 617 need to be understood.Abstract – Alloy 617 is among the primary candidates for very high temperature reactor heat exchangers anticipated for use up to 950ºC. Elevated temperature properties of this alloy and the mechanisms responsible for the observed tensile, creep and creep-fatigue behavior have been characterized over a wide range of test
CREEP-FATIGUE BEHAVIOR OF ALLOY 617 AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURE July 2023 Peijun Hou, Yanli Wang, Ting-Leung Sham. DISCLAIMER . life at critical locations of high-temperature component, in an attempt to develop the current structural designs, is necessary to be addressed.Furthermore, elastic follow-up caused by a mixed . Nickel-based superalloy 617M was subjected to high cycle fatigue loading at 973 K. The tests were conducted at a constant amplitude of alternating stresses at different stress ratios (R). A constant life diagram, also called as Haigh diagram, was generated for finite life criteria of 107 cycles. Fatigue endurance limit of 320 MPa was recorded at R = − 1. At the .
In order to understand the baseline high-temperature creep-fatigue behavior for Alloy 617, this study presents the creep-fatigue behavior of Alloy 617 base metal and weldments in air at 900 °C. Tests were performed with fully-reversed axial strain control at total strain range of 0.6%, 1.2%, and 1.5% and peak tensile hold time of 60, 180, and .High Temperature Nuclear Reactor (VHTR), expected to have an outlet temperature as high as 950°C. Acceptance of Alloy 617 in Section III of the ASME Code for nuclear construction requires a detailed understanding of the creep-fatigue behavior. Initial creep-fatigue work on Alloy 617 suggests a more Alloy 617 is the leading candidate material for an intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) application of the Very High Temperature Nuclear Reactor (VHTR), expected to have an outlet temperature as high as 950 degrees C. Acceptance of Alloy 617 in Section III of the ASME Code for nuclear construction requires a detailed understanding of the creep-fatigue .Alloy 617 is the leading candidate material for an intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) of the very high temperature reactor (VHTR), expected to have an outlet temperature as high as 950°C. Acceptance of Alloy 617 in Section III of the ASME Code for nuclear construction requires a detailed understanding of the creep-fatigue behavior.
Therefore, the creep-fatigue behavior of Alloy 617 requires systematic investigation for its qualification as the structural material for IHX applications in VHTR. . High-temperature creep-fatigue behavior of alloy 617. Metals (2018) Wright JK, Carroll LJ, Sham TL, Lybeck NJ, Wright RN. Determination of the creep-fatigue interaction diagram .
Yoon et al. performed high-temperature creep-fatigue crack growth tests on 1.25Cr–0.5Mo steel with waveforms containing a hold time at maximum load. The authors investigated the effect of applying an OL prior to each hold time. . Alloy 617 exhibits power law creep behavior under sustained loads at the temperatures of interest (Benz et al . Alloy 617 is the leading candidate material for an intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) application of the Very High Temperature Nuclear Reactor (VHTR), expected to have an outlet temperature as high as 950 degrees C. Acceptance of Alloy 617 in Section III of the ASME Code for nuclear construction requires a detailed understanding of the creep-fatigue behavior.
thermal stability as well as high temperature creep and oxidation resistance. Based on these material requirements, the nickel base alloy UNS N06617, . fatigue and creep-fatigue behavior of Alloy 617 has been carried out at multiple strain ranges at temperatures of 850 and 950°C to support this creep- Conference: NOTCH EFFECT ON CREEP-FATIGUE BEHAVIOR OF ALLOY 617 AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURE . High-temperature reactor structural components are often under the complex multiaxial creep-fatigue (CF) loading conditions throughout the lifetime because of geometric and/or metallurgical discontinuities and complex loading paths. To .
This paper presents the high-temperature creep-fatigue testing of a Ni-based superalloy of Alloy 617 base metal and weldments at 900 °C. Creep-fatigue tests were conducted with fully reversed axial strain control at a total strain range of 0.6%, 1.2%, and 1.5%, and peak tensile hold time of 60, 180, and 300 s. The effects of different constituents on the .
Test results are shown for Alloy 617 fatigue and creep-fatigue (without the gauge for load-line displacement measurements), as well as creep-fatigue of Alloy 709, which was performed with the completed test setup, allowing for crack length and load-line displacement monitoring. . Creep and Environmental Effects on High Temperature Creep .
Creep-fatigue testing of nickel alloy 617 base metal and fusion weldments was performed at temperatures of 800 and 1000°C in air in support of ASME BPV Sec III code qualification of alloy 617 for the Next-Generation Nuclear Plant. Cyclic loading was performed in strain control with a trapezoidal waveform and was fully reversed. Creep was introduced into . Abstract. High-temperature reactor structural components are often under the complex multiaxial creep-fatigue (CF) loading conditions throughout the lifetime because of geometric and/or metallurgical discontinuities and complex loading paths. To assess the multiaxial CF deformation behavior and to evaluate the CF design rules in the ASME BPVC Section III, . Previous studies of the creep-fatigue behavior of Alloy 617 at 950 °C indicate that the fatigue life is reduced when a constant strain dwell is added at peak tensile strain.[2-5] This results from the combination of faster crack initiation occurring at surface-connected grain boundaries due to oxidation from the air environment along with . This paper presents the high-temperature creep-fatigue testing of a Ni-based superalloy of Alloy 617 base metal and weldments at 900 °C. . Temperature effect on the creep behavior of alloy 617 in air and helium environments. Woo-Gon Kim Jae-Young Park Gyeong-Geun Lee Sung-Deok Hong Yong-Wan Kim. Materials Science, Engineering. 2014; 23.
Alloy 617 is the primary candidate material for the heat exchanger of a very high temperature gas cooled reactor intended to operate up to 950°C. . comments were received indicating that there was insufficient knowledge of the creep and creep-fatigue behavior of Alloy 617 welds. In this report the results of recent experiments and analysis . The nickel-base superalloy, alloy 617 M is considered as a candidate material for key components of the advanced ultra-supercritical (AUSC) power plants owing to its excellent high-temperature strength, good creep and corrosion resistance. The alloy is intended for target steam conditions of 993 K and 310 kg/cm2, and is the most favourable material for high . Inconel Alloy 617 is a high temperature creep and corrosion resistant alloy and is a leading candidate for use in Intermediate Heat Exchangers (IHX) of the Next Generation Nuclear Plants (NGNP). The IHX of the NGNP is expected to experience operating temperatures in the range of 800 degrees - 950 degrees C, which is in the creep regime of Alloy .
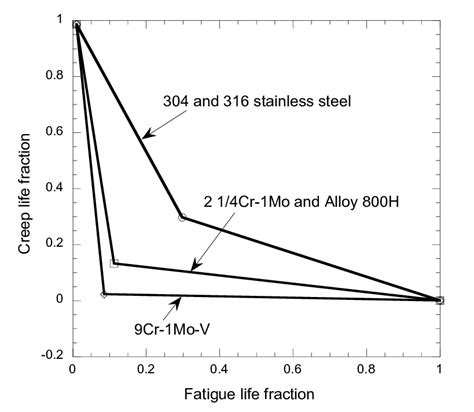
high temp creep fatigue interaction
Caesars Entertainment is more than just a hotel and casino company. It is a world of entertainment, where you can enjoy stunning shows, gourmet dining, upscale casinos, and luxurious accommodations. Whether you want to indulge in elegance, have some fun, or earn rewards, Caesars Entertainment has something for you.
high-temperature creep-fatigue behavior of alloy 617|617 creep fatigue